Bar chart: Difference between revisions
From Planfix
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The bar chart is created from report data and consists of two axes: | The bar chart is created from report data and consists of two axes: | ||
Horizontal axis (X) — represents categories (e.g., days of the week, project names). | *Horizontal axis (X) — represents categories (e.g., days of the week, project names). | ||
Vertical axis (Y) — represents numerical values (e.g. number of tasks completed, hours worked, sales amounts). | *Vertical axis (Y) — represents numerical values (e.g. number of tasks completed, hours worked, sales amounts). | ||
To ensure that relevant data is displayed, use grouping and sorting. | To ensure that relevant data is displayed, use grouping and sorting. | ||
==Setup== | ==Setup== | ||
Revision as of 07:05, 15 July 2025
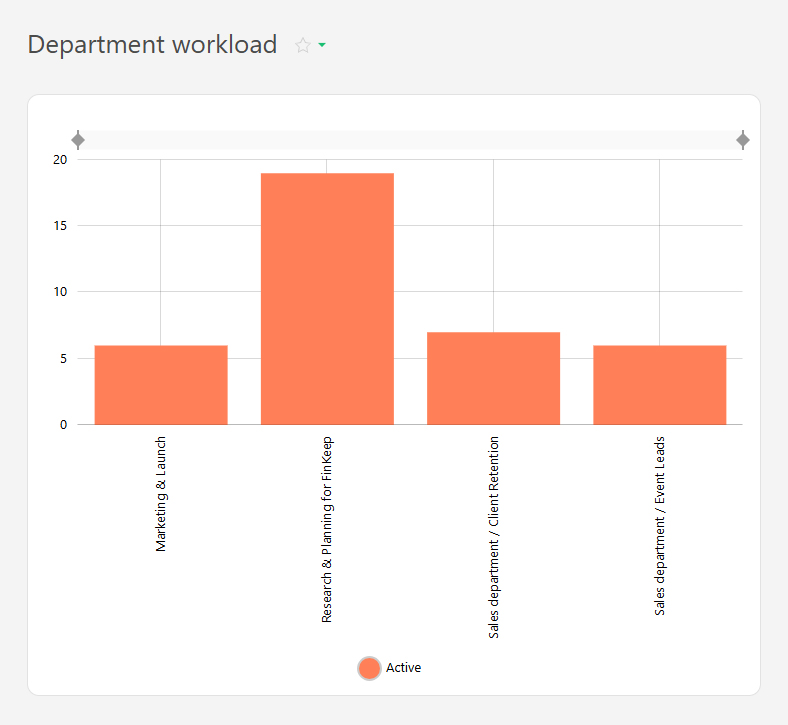
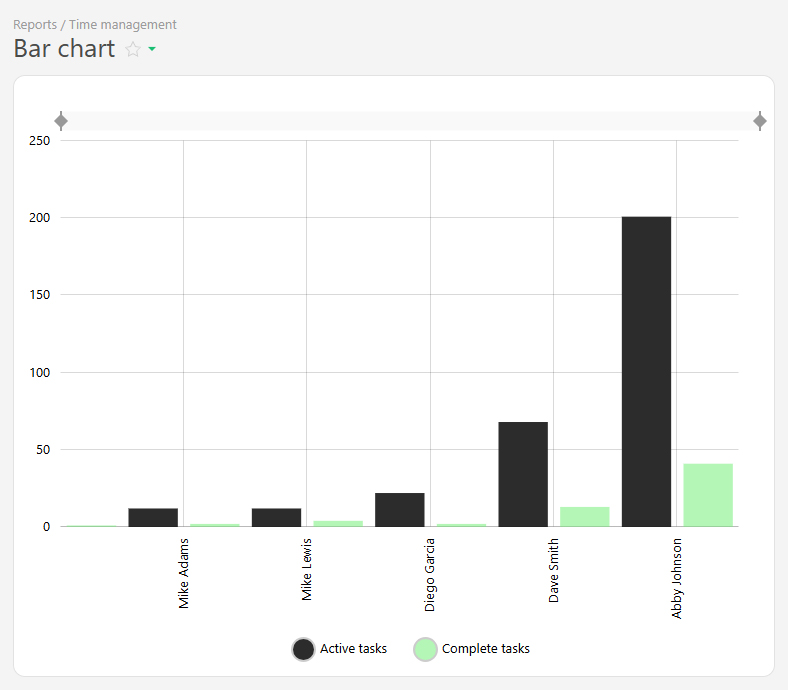
The Bar chart is a chart type available in reports. It displays data as vertical bars, with each bar representing a value or quantity that corresponds to a specific category. Bar charts are useful for comparing data.
For example, the active and completed tasks per employee for a month can be displayed:
 The bar chart is created from report data and consists of two axes:
The bar chart is created from report data and consists of two axes:
- Horizontal axis (X) — represents categories (e.g., days of the week, project names).
- Vertical axis (Y) — represents numerical values (e.g. number of tasks completed, hours worked, sales amounts).
To ensure that relevant data is displayed, use grouping and sorting.
Setup
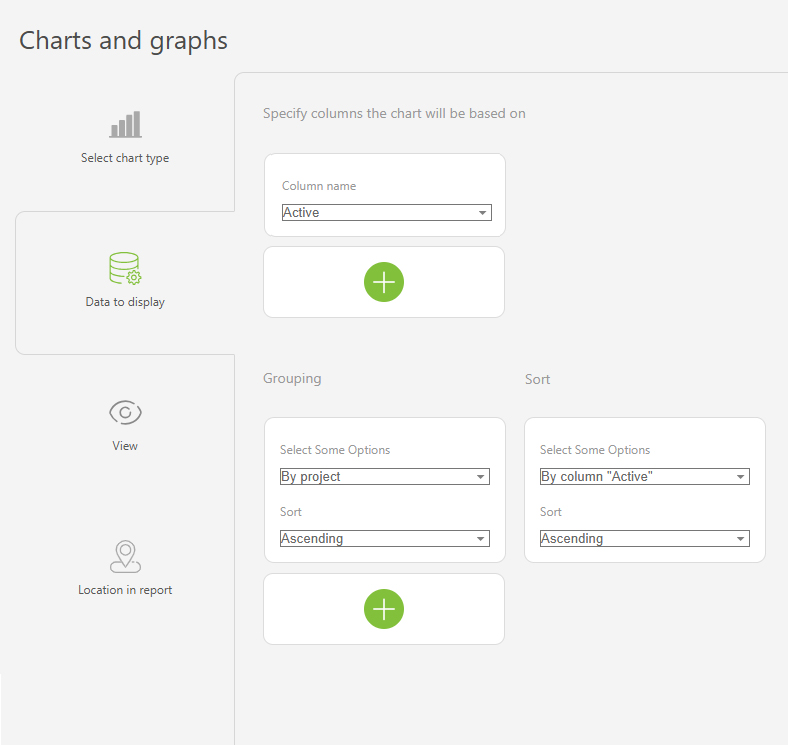
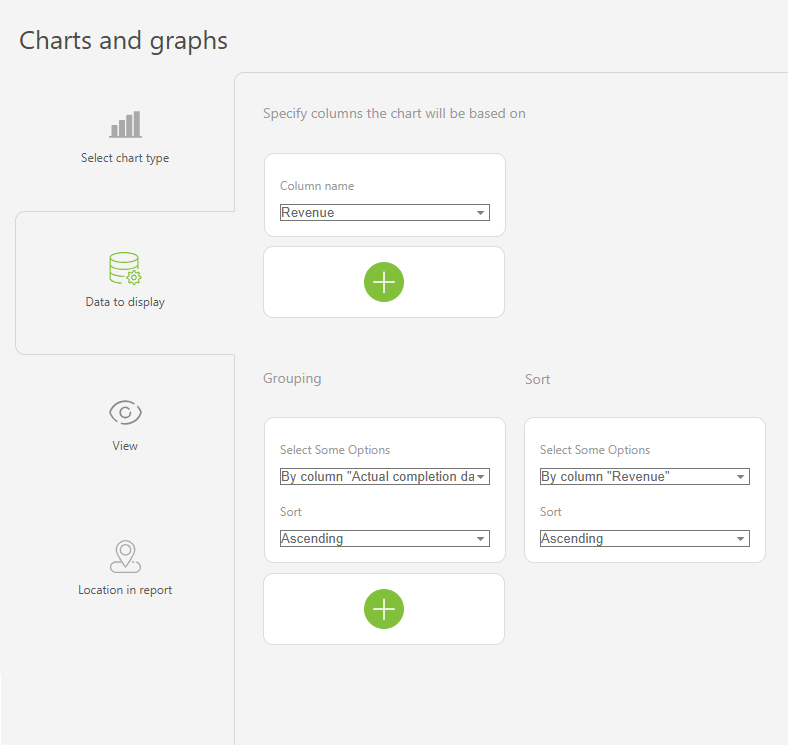
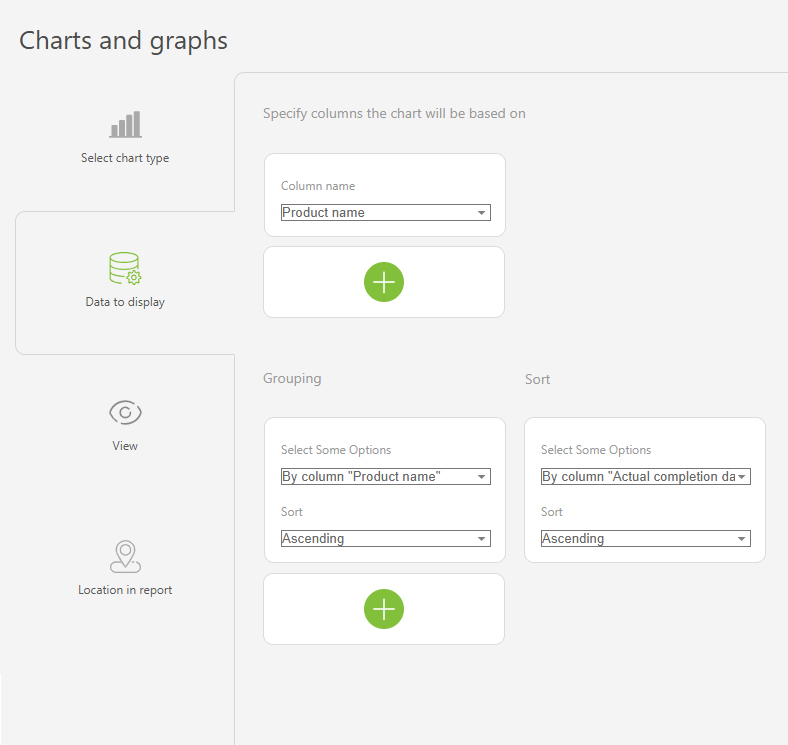
- In the "Report view", add the columns that will form the bar chart.
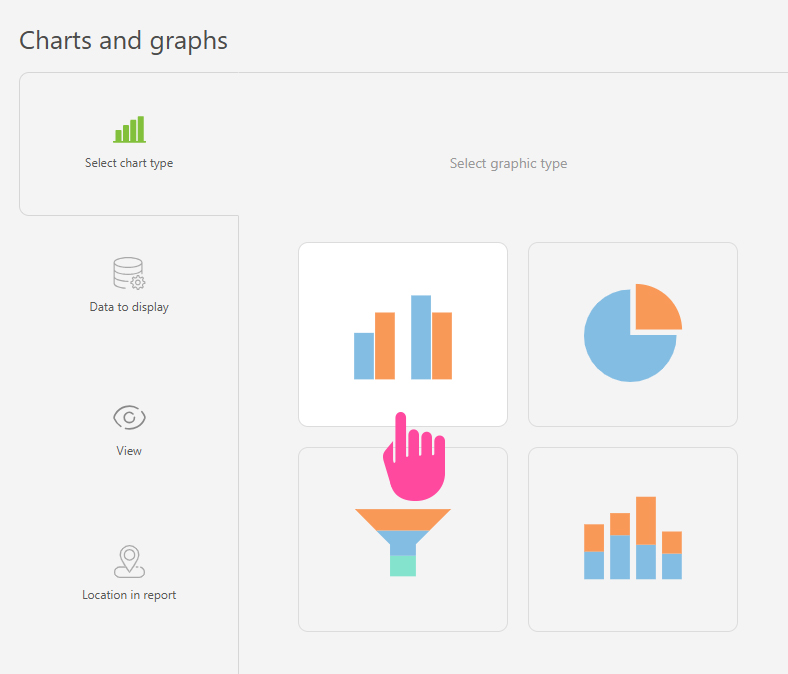
- Go to the "Charts and graphs" section and add a new "Bar" type chart:
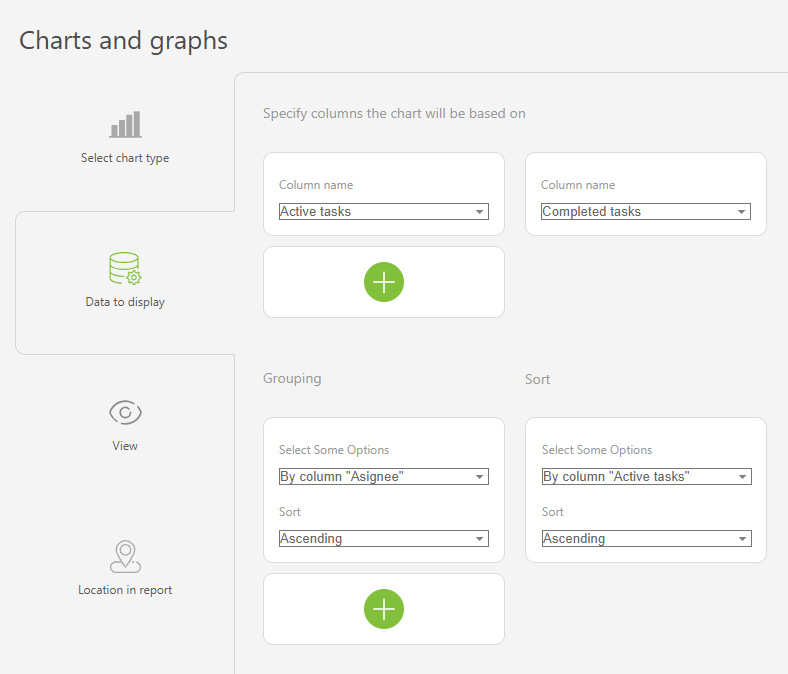
- In "Data to display", set the following:
- Columns on which the chart will be based: "Active tasks", "Completed tasks".
- Grouping: By the "Assignee" column.
- Sort: by the "Active tasks" column, ascending.
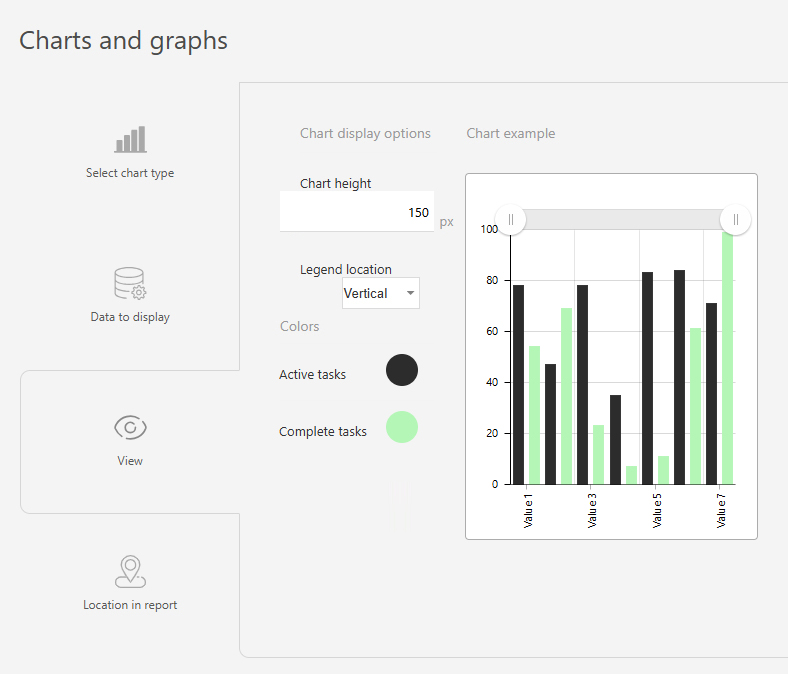
- In the "View" section, you configure how the chart is displayed:
- "Chart height" — defines the height of the chart in pixels.
- "Legend location" — controls how the axis labels are displayed. Tip: Use "Vertical" for longer labels to save space, "Horizontal" is best for shorter labels.
- "Colors" — helps to differentiate between data groups using different colors.
- Save the chart and run the report to view it.
Use case examples
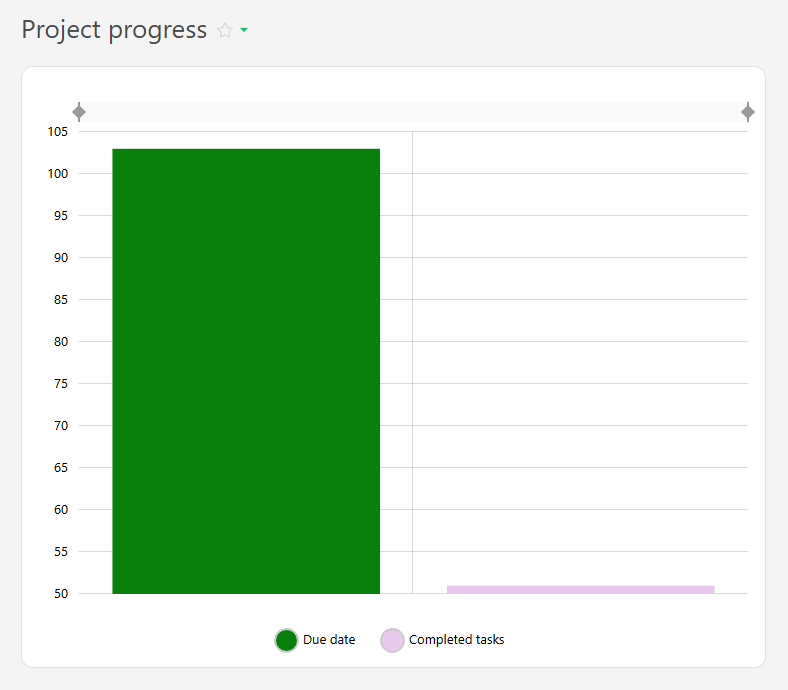
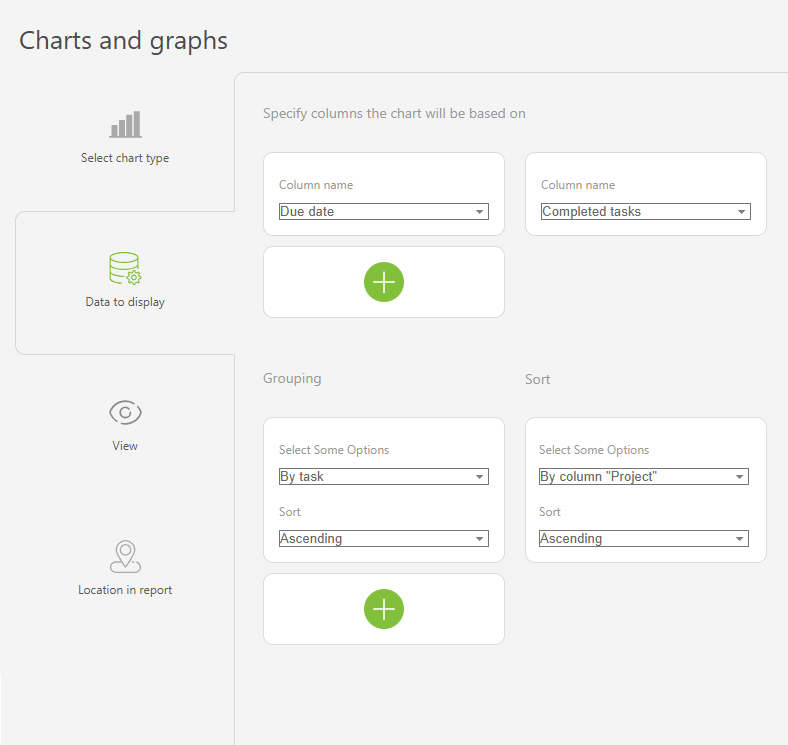
- Project progress
- Revenue by month
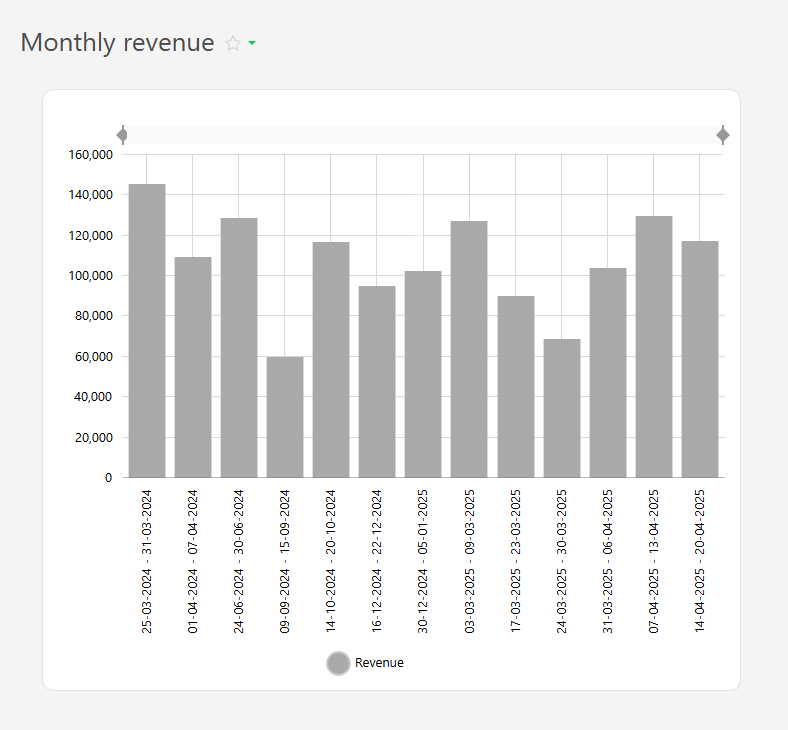
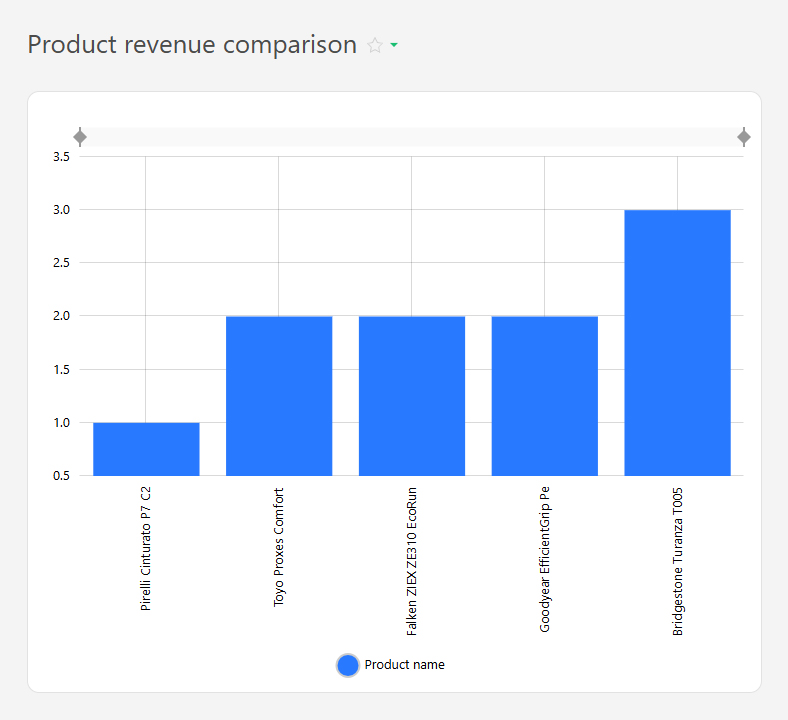
- Revenue by individual products
- Department workload level